Diamond is the hardest natural substance known to man. Many are billions of years old, and their remarkable and beautiful physical properties have made them desirable for centuries.
However, In recent years, the traditional diamond industry has come under criticism for its ethical and environmental challenges as consumers become more aware of the knock-on effect of the notorious ‘blood diamond’ industry. As such, there has been a move towards lab grown diamonds — the sustainable counterpart to traditional earth-mined diamonds.
This shift is transforming the diamond industry, putting lab grown diamonds in the spotlight as an alternative for conscious consumers. But the big question is: are lab grown diamonds more ethical?
The History of Diamond Mining
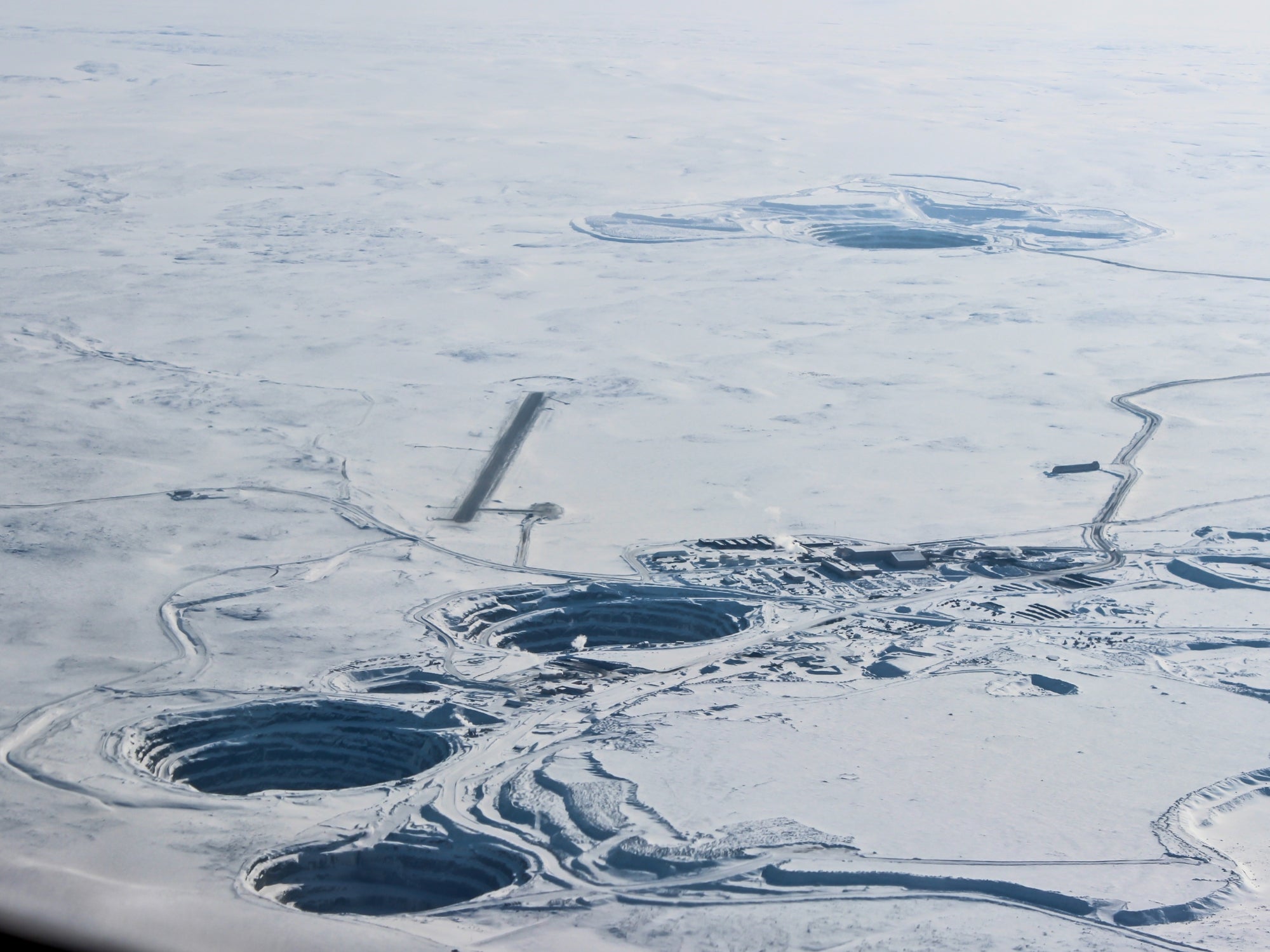
The story of diamonds began as early as the 4th Century BC in India. From here until the late 1800s, India was believed to be the only diamond source on earth. This all changed dramatically when diamonds were discovered in South Africa in 1867, leading to a diamond rush — and the beginning of the multi-billion dollar diamond industry we know today.
Diamonds are extracted from deep within the Earth’s crust, often under harsh conditions, where they have formed over billions of years. These rough diamonds are then sent to diamond traders across the globe to be cut, polished and sold.
Why are Diamonds Unethical?
Diamonds often come from countries rich in natural resources but economically impoverished. "Blood diamonds," mined in conflict zones and sold to fund wars, became a massive problem in the late 20th century, particularly in Africa. Mining was linked to human rights abuses, including forced labour and violence.
In 2003, ‘The Kimberley Process’ was introduced — a globally recognised diamond certification process intended to clean up the industry by ensuring responsible diamond sourcing. While improvements have been made, the process has been criticised for inefficiency. Some countries have remained non-compliant, and many untraceable diamonds continue to slip through the net.
As a result, natural diamonds are widely considered unethical, making them a morally dubious option for jewellery.

The Emergence of Lab-Grown Diamonds
The first lab grown diamonds were created in the 1950s, but the industry has only taken off in the last few decades. While diamonds have always been popular, a heightened awareness around the ethical implications of the diamond trade coupled with the global drive for better environmental practices has rocketed lab grown diamonds into the limelight as a sustainable alternative.
Are Lab Grown Diamonds Eco-Friendly?
Created using methods like High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD), lab grown diamonds replicate the natural process of diamond formation in a significantly sped-up process (a matter of weeks or months instead of billions of years). These diamonds are chemically identical to natural ones and have virtually indistinguishable differences, offering consumers a more affordable and sustainable option. The differences between CVD vs HPHT diamonds are minimal and focus mainly on the process rather than the result.
Lab-grown diamonds are assessed by gemologists and valued similarly to traditional diamonds, using the 4Cs method (cut, colour, clarity, and carat). Our diamond clarity guide offers more detail on this process.
Ethical Advantages of Lab-Grown Diamonds
The ethical advantages of choosing jewellery with lab grown diamonds are plentiful. With plenty of controversy surrounding the unethical earth mined diamond industry, here are some of the benefits of lab grown alternatives:
No community displacement: Diamond mines are continually being discovered, with many communities displaced and habitats destroyed in the process. Lab-grown diamonds are created in a controlled laboratory environment to avoid these negative impacts.
Ethical supply chain: Lab grown diamonds are produced in traceable factories, meaning their journey to the finished product is fully transparent. Earth mined diamond processes often result in enforced or child labour, which is usually hard to trace and abolish.
Conflict-free:Lab grown diamonds are considered more ethical due to being conflict-free; they are not mined in war zones or used to fund armed conflicts.
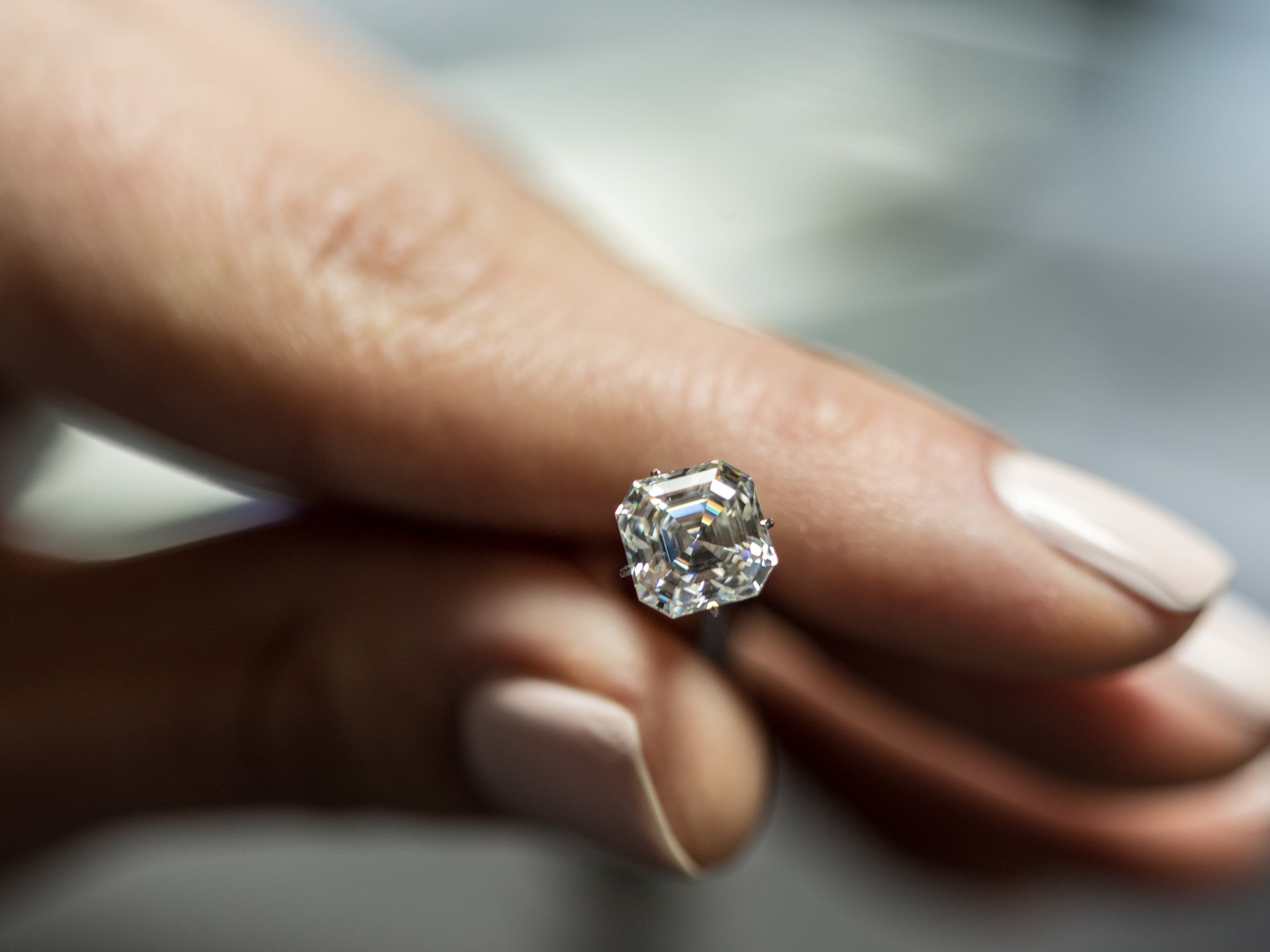

Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Aside from the ethical advantages of lab grown diamonds mentioned above, there are significant environmental and sustainable advantages of lab grown diamonds, too. Some of these include:
Lower Environmental Impact
Lab grown diamonds are considered better for the environment, as they require significantly less land excavation, water usage, and energy than diamond mining, which causes deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution. The process of mining diamonds can also cause large-scale environmental degradation, such as soil erosion and water contamination.
Lower Carbon Footprint
Lab grown diamonds are significantly more eco-friendly and have a smaller carbon footprint than mined diamonds. Although the lab process involves using heat and machinery, these can be made with renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, reducing their environmental impact. In contrast, diamond mining involves heavy machinery, fossil fuels, and long transportation routes, leading to much higher carbon emissions.
Water Conservation
A vast amount of water is used in diamond mining, often depleting and contaminating local water sources. By contrast, significantly less water is used in a lab setting, lowering the environmental impact of lab grown diamonds.
No Mining Waste
Earth mined diamonds generate a lot of waste in the mining process, such as leftover earth, rocks, and materials from the extraction process, often causing damage to the local environment. By contrast, lab diamonds are more sustainable, as they’re made in a highly controlled environment where materials can be handled responsibly.
Economic Implications
Lab grown diamonds are generally more affordable than natural diamonds. The cost of production is lower, primarily because lab grown diamonds are not subject to the same extraction costs, transportation, or geopolitical risks that come with mining.
As a result, lab diamonds are sustainable and an appealing option for those who want the look and feel of a diamond at an accessible price point.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
While some consumers have been sceptical about lab grown diamonds, trends are beginning to shift. Natural diamonds still retain a level of rarity as only a finite amount is produced by the earth, compared to the limitless potential to create lab grown diamonds.
However, lab grown diamonds have grown traction in recent years, particularly for their eco-friendly appeal with the younger consumer market.
People are more inclined than ever to support sustainable brands, such as Fyne, and as a result, the market for lab grown diamonds is expanding.
The Future of the Diamond Industry
The diamond market continues to evolve, and as technologies for creating lab grown diamonds advance, their popularity will likely continue to grow alongside it. Due to modern-day demands for ethical options, sustainable lab grown diamonds will likely begin to occupy more and more of the market share.
The environmental impact of lab grown diamonds is far less than earth mined diamonds, and standards continue to improve as companies invest in the most sustainable and innovative production methods.
It’s likely, too, that traditional diamond miners will adopt greener practices to meet the demands of ever-growing conscious consumers. Despite this, it’s not probable that earth mined diamonds will ever reach the sustainability and ethics demonstrated by the lab-grown diamond market.
At Fyne, we firmly believe that beauty doesn’t have to cost the earth, which is why our entire jewellery collection features certified, traceable, and sustainable lab grown diamonds. To us, lab grown diamonds represent a future where ethics and timeless beauty go hand in hand.